 Impact Methods: Explore what we did
Impact Methods: Explore what we did
In order to dig more deeply into the Student Impact findings regarding fresh start schools and full school turnarounds, we examined student demographic characteristics as well as certain school characteristics to determine whether these factors accounted for any of the observed differences in performance between fresh starts and full school turnarounds.
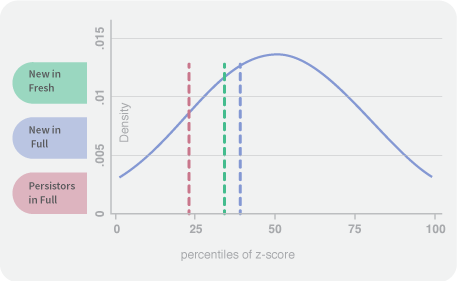
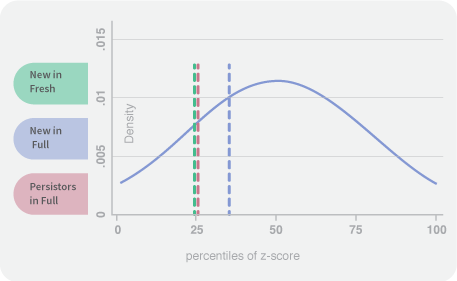
Fresh start schools and full school turnarounds are similar in terms of racial composition, percentage of English Language Learners, and percentage of Special Education students. Fresh start schools are likely to have fewer students eligible for Free/Reduced Price Lunch, although this difference is not statistically significant.
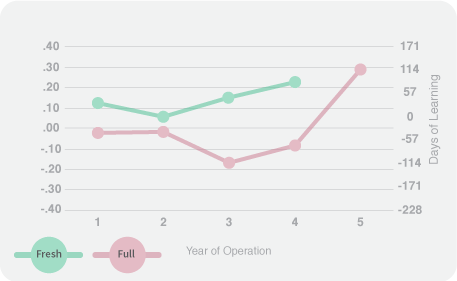
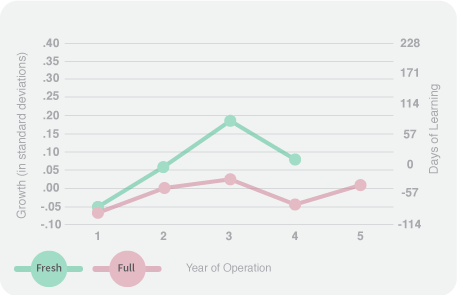
Students in CRM schools operated by a CMO from the local community exhibit on average 154 additional days of learning in reading and 171 additional days of learning on average in math, compared to students in CRM schools operated by non-local CMOs. Fresh start schools were more likely to be operated by a local CMO.
Board activity, defined by number of meetings per year, is negatively associated with student learning, perhaps because boards of struggling schools feel the need to meet more frequently. Having an additional board meeting in a given year is associated with 205 fewer days of learning for each student on average in reading and 245 fewer days of learning for each student on average in math. Fresh start schools had less frequent board meetings compared to full school turnarounds.
Eleven CRM schools experience at least one leadership turnover during the course of the evaluation. Having a principal turnover in a given year is associated with 57 fewer days of learning in reading for each student on average and 188 fewer days of learning in math for each student on average, although only the math finding is statistically significant here.
An increase of one increment on the PMO scale is associated with 274 additional days of learning in reading and 29 additional days of learning in math for students in fresh start CRM schools. Fresh starts are found to have a significantly higher PMO scores than full school turnarounds, suggesting higher implementation quality in the fresh start CRM schools. Additionally, the association between PMO score and growth is stronger for fresh starts than for full school turnarounds.
An increase of one increment on the PMO scale is associated with 234 additional days of learning in reading and 17 additional days of learning in math for students in CRM full school turnarounds.
Go back to the main Student Impact page or explore the impact data by individual states: Louisiana and Tennessee
